# Zustand
Zustand (opens new window) 是一个 React 状态管理的库,它比 Redux (opens new window) 更简单、更轻便、更灵活,使用起来就像在用 React hook 一样,没有 Redux 那么多的样板代码。
# 安装
$ pnpm add zustand
# 基础用法
// useBearStore.ts
import { create } from 'zustand';
type BearStore = {
bears: number;
increase: () => void;
reset: () => void;
};
const useBearStore = create<BearStore>()((set) => ({
bears: 0,
increase: () => set((state) => ({ bears: state.bears + 1 })),
reset: () => set({ bears: 0 }),
}));
export default useBearStore;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
📢 在 Typescript 中,
create方法需要定义 store 的类型和使用 curry 函数,详情请参考 TypeScript Guide (opens new window)。
在 React 组件中使用
import useBearStore from '@/store/useBearStore';
function BasicPage() {
// 推荐使用 selector,避免不必要的渲染
const bears = useBearStore((state) => state.bears);
const increase = useBearStore((state) => state.increase);
const reset = useBearStore((state) => state.reset);
// 如果确定不会引起不必要的渲染,也可以直接这么使用
// const { bears, increase, reset } = useBearStore();
return (
<div>
<div>{bears}</div>
<div>
<Button onClick={increase}>增加</Button>
<Button onClick={reset}>重置</Button>
</div>
</div>
);
}
export default BasicPage;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
就是这么简单,就像使用普通的 React Hook 一样。
# Selector
如上面的例子所示,使用 store 的时候,zustand 推荐使用 selector,这样可以避免不必要的渲染。
const bears = useBearStore((state) => state.bears);
const increase = useBearStore((state) => state.increase);
2
如果有很多的状态值,不想重复这些样板代码,可以定义一个自动生成 selector 的函数: createSelectors
import { StoreApi, UseBoundStore } from 'zustand'
type WithSelectors<S> = S extends { getState: () => infer T }
? S & { use: { [K in keyof T]: () => T[K] } }
: never
const createSelectors = <S extends UseBoundStore<StoreApi<object>>>(
_store: S,
) => {
let store = _store as WithSelectors<typeof _store>
store.use = {}
for (let k of Object.keys(store.getState())) {
(store.use as any)[k] = () => store((s) => s[k as keyof typeof s])
}
return store
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
然后就使用这个函数来简化代码, 更多详情请参考 Auto Generating Selectors (opens new window).
const useBearStoreSelector = createSelectors(useBearStore);
const bears = useBearStore.use.bears()
const increment = useBearStore.use.increment()
2
3
4
很好奇为什么 zustand 把这种解决方案写在文档了,而不直接写成 API 或者中间件呢?
# useShallow
Zustand 使用 Object.is (opens new window) 判断 selector 返回的状态值是否发现了变化,对于 primitive 类型的值是没有问题的,但是如果 selector 返回的对象类型,可能会导致不必要的渲染,这个时候可以使用 useShallow (opens new window) 来比较值是否真的发生了变化。
// useMeals.ts
import { create } from 'zustand';
type MealsStore = {
papaBear: string;
mamaBear: string;
littleBear: string;
};
const useMeals = create<MealsStore>()(() => ({
papaBear: 'large porridge-pot',
mamaBear: 'middle-size porridge pot',
littleBear: 'A little, small, wee pot',
}));
export default useMeals;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
组件使用
import useMeals from '@/store/useMeals';
import { useShallow } from 'zustand/react/shallow';
const SelectorPage = () => {
const names = useMeals(useShallow((state) => Object.keys(state)));
const changePapaBear = () => {
useMeals.setState({
papaBear: 'a large pizza',
});
};
return (
<div className={styles.container}>
<div style={{ marginBottom: 30, fontSize: 30 }}>{names.join(', ')}</div>
<Button onClick={changePapaBear}></Button>
</div>
);
};
export default SelectorPage;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
修改 papaBear 的值并不影响 Object.keys(state) 的值,但是如果不使用 useShallow 会导致 Object.keys(state) 每次返回一个新数组,Object.is (opens new window) 判断 false,从而导致组件重新渲染。
需要注意的是,useShallow (opens new window) 和 React PureComponent 一样是浅层次的比较,如果需要进行深层次的比较可以自定义相等函数,比如使用 lodash 的 isEqual (opens new window) 函数。
const treats = useBearStore(
(state) => state.treats,
(oldTreats, newTreats) => _.isEqual(oldTreats, newTreats)
)
2
3
4
# 计算属性
Zustand 没有像 Vuex (opens new window)、Pinia (opens new window) 一样提供直接的计算属性,但是有两种方法处理这个问题。
- 使用函数
- 自定义 hook
比如下面要计算 fullName
// useComputedStore.ts
import { create } from 'zustand';
type UserStore = {
firstName: string;
lastName: string;
setFirstName: (firstName: string) => void;
setLastName: (lastName: string) => void;
};
const useComputedStore = create<UserStore>()((set, get) => ({
firstName: '',
lastName: '',
setFirstName: (firstName: string) => set({ firstName }),
setLastName: (lastName: string) => set({ lastName }),
}));
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 使用函数
type UserStore = {
firstName: string;
lastName: string;
setFirstName: (firstName: string) => void;
setLastName: (lastName: string) => void;
fullName: () => string;
};
const useComputedStore = create<UserStore>()((set, get) => ({
firstName: '',
lastName: '',
setFirstName: (firstName: string) => set({ firstName }),
setLastName: (lastName: string) => set({ lastName }),
fullName: () => get().firstName + ' ' + get().lastName,
}));
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
在组件里使用的时候要注意,要在 selector 里调用函数,而不是 render 里调用函数
function FullName() {
const fullName = useComputedStore((state) => state.fullName());
return (
<div style={{ marginBottom: 30, fontSize: 30 }}>FullName: {fullName}</div>
);
}
2
3
4
5
6
# 自定义 Hook
export const useFullName = () => {
const firstName = useComputedStore((state) => state.firstName);
const lastName = useComputedStore((state) => state.lastName);
const fullName = firstName + ' ' + lastName;
return { fullName };
};
2
3
4
5
6
在组件里使用这个 hook
import { useFullName } from '@/store/useComputedStore';
function FullName() {
const { fullName} = useFullName();
return (
<div style={{ marginBottom: 30, fontSize: 30 }}>FullName: {fullName}</div>
);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
关于计算属性的更多讨论,请参考 Using getter to calculate computed values (opens new window)
# 异步
Zustand 使用异步也非常简单,直接定义异步函数即可,无需额外的配置。组件使用也没有区别。
// useUserStore.ts
import { getCurrentUserReq } from '@/services/user';
import { create } from 'zustand';
type UserStore = {
user?: API.UserInfo;
getUser: () => void;
};
const useUserStore = create<UserStore>()((set) => ({
user: undefined,
getUser: async () => {
const { data, success } = await getCurrentUserReq();
if (success) {
set({ user: data });
}
},
}));
export default useUserStore;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# 非响应式
useBearStore() 作为 React Hook 只能用于 React 组件,怎么在 React 组件外面使用 zustand 呢?Zustand 提供了下面的 API 来处理这个问题:
getInitialState- 获取状态值getState- 获取状态值setState- 设置状态值subscribe- 订阅状态的变化
const increase = () => {
const preBears = useBearStore.getState().bears;
useBearStore.setState({ bears: preBears + 1 });
};
const reset = () => {
useBearStore.setState({ bears: 0 });
};
const unsub = useBearStore.subscribe((cur, pre) => {
console.log(cur, pre);
});
// 取消订阅
unsub();
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
📢 上面的例子中是
useBearStore而不是useBearStore()
此外 Zustand 提供了 createStore API 专用于非响应式的情形
import { createStore } from 'zustand/vanilla'
const store = createStore((set) => ...)
const { getState, setState, subscribe, getInitialState } = store
export default store
2
3
4
5
6
这种情况如果想转换为响应式,使用 useStore hook
import { useStore } from 'zustand'
import { vanillaStore } from './vanillaStore'
const useBoundStore = (selector) => useStore(vanillaStore, selector)
2
3
4
# Slices 模式
随着功能越来多,store 会变得越来越大,越来越难维护。这个时候你可以把 store 分成更小的 slices,然后将 slices 组合起来
import { create, StateCreator } from 'zustand';
interface BearSlice {
bears: number;
addBear: () => void;
eatFish: () => void;
}
interface FishSlice {
fishes: number;
addFish: () => void;
}
interface SharedSlice {
addBoth: () => void;
getBoth: () => void;
}
const createBearSlice: StateCreator<
BearSlice & FishSlice,
[],
[],
BearSlice
> = (set) => ({
bears: 0,
addBear: () => set((state) => ({ bears: state.bears + 1 })),
eatFish: () => set((state) => ({ fishes: state.fishes - 1 })),
});
const createFishSlice: StateCreator<
BearSlice & FishSlice,
[],
[],
FishSlice
> = (set) => ({
fishes: 0,
addFish: () => set((state) => ({ fishes: state.fishes + 1 })),
});
const createSharedSlice: StateCreator<
BearSlice & FishSlice,
[],
[],
SharedSlice
> = (set, get) => ({
addBoth: () => {
// you can reuse previous methods
get().addBear();
get().addFish();
// or do them from scratch
// set((state) => ({ bears: state.bears + 1, fishes: state.fishes + 1 })
},
getBoth: () => get().bears + get().fishes,
});
const useBoundStore = create<BearSlice & FishSlice & SharedSlice>()((...a) => ({
...createBearSlice(...a),
...createFishSlice(...a),
...createSharedSlice(...a),
}));
export default useBoundStore;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
# Store 混用
Slices 模式只是将一个复杂的 store 先拆分再合并,我更喜欢 Pinia (opens new window) 的模式:直接在 store 里使用另外的 stores。
上面的 Slices 模式可以这样使用 useFishStore 和 useMixStore 是独立的 store.
// useFishStore.ts
import { create } from 'zustand';
type FishStore = {
fishes: number;
addAFish: () => void;
substractAFish: () => void;
};
const useFishStore = create<FishStore>()(
(set, get) => ({
fishes: 0,
addFish: () => set({ fishes: get().fishes + 1 }),
substractFish: () => set({ fishes: get().fishes - 1 }),
})
);
export default useFishStore;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
在其它的 store 里使用 useFishStore
// useMixStore.ts
import { create } from 'zustand';
import useFishStore from './useFishStore';
type BearStore = {
bears: number;
addBear: () => void;
eatFish: () => void;
};
const useMixStore = create<BearStore>()((set) => ({
bears: 0,
addBear: () => set((state) => ({ bears: state.bears + 1 })),
eatFish: () => {
const fishes = useFishStore.getState().fishes;
useFishStore.setState({ fishes: fishes - 1 });
// 或者
// useFishStore.getState().substractFish();
},
}));
export default useMixStore;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# 中间件
Zustand 提供了多个中间件,来增强功能、简化代码
# Combine
前面提到在 Typescript 中,zustand 的 create 方法需要定义 store 的类型和使用 curry 函数,但是通过 combine 中间件就免去了这些操作
import { create } from 'zustand'
import { combine } from 'zustand/middleware'
const useBearStore = create(
combine({ bears: 0 }, (set) => ({
increase: (by: number) => set((state) => ({ bears: state.bears + by })),
})),
)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
useBearStore 能被正确推导出类型。
# Immer
Zustand 和 Redux 一样都是合并 state,要求不能直接修改 state,这对应修改嵌套对象不是很方便,所以 Zustand 和 Redux 一样使用 Immer (opens new window),来简化修改嵌套对象的值
使用 Immer 库
import { produce } from 'immer';
import { create } from 'zustand';
type BeeStore = {
lush: { forest: { bees: number } };
addBees: (by: number) => void;
};
const useBeeStore = create<BeeStore>()((set) => ({
lush: { forest: { bees: 0 } },
addBees: (by) =>
set(
produce((state) => {
state.lush.forest.bees += by;
}),
),
}));
export default useBeeStore;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
使用 Immer 中间件
import { create } from 'zustand'
import { immer } from 'zustand/middleware/immer'
type BeeStore = {
lush: { forest: { bees: number } };
addBees: (by: number) => void;
};
const useBeeStore = create<BeeStore>()(
immer((set) => ({
lush: { forest: { bees: 0 } },
addBees: (by) =>
set((state) => {
state.lush.forest.bees += by;
}),
})),
);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# SubscribeWithSelector
Zustand 的 subscribe 方法有一个缺陷,store 的任何改变都会触发 subscribe 回调,如果你只想某个值变化时才触发 subscribe 回调,可以使用 subscribeWithSelector 中间件
type BearStore = {
bears: number;
bees: number;
};
const useBearStoreWithSelector = create<BearStore>()(
subscribeWithSelector(() => ({
bears: 0,
bees: 0,
})),
);
const unsub = useBearStoreWithSelector.subscribe(
(state) => state.bears,
(curBears, preBears) => {
console.log(curBears, preBears);
},
);
// 取消订阅
unsub()
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
使用 subscribeWithSelector 中间件也支持订阅整个 state
const unsub = useBearStoreWithSelector.subscribe(
(curState, preState) => {
console.log(curState, preState);
},
);
2
3
4
5
# Persist
使用 persist 中间件持久化 store 数据,你可以使用任意的储存库,比如 localStorage (opens new window) (默认)、sessionStorage (opens new window)、async-storage (opens new window)。
持久化数据的好处就是刷新浏览器时,store 能保持之前的状态。
import { create } from 'zustand';
import { createJSONStorage, persist } from 'zustand/middleware';
type FishStore = {
fishes: number;
addAFish: () => void;
};
const useFishStore = create<FishStore>()(
persist(
(set, get) => ({
fishes: 0,
addAFish: () => set({ fishes: get().fishes + 1 }),
}),
{
name: 'food-storage', // name of the item in the storage (must be unique)
storage: createJSONStorage(() => sessionStorage), // (optional) by default, 'localStorage' is used
},
),
);
export default useFishStore;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
使用时或者状态变化时会同步数据到 sessionStorage
初始值
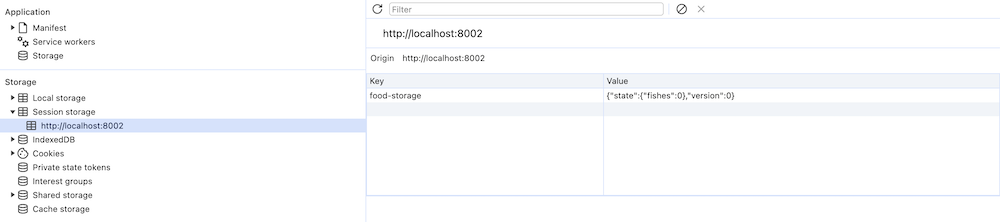
变化后
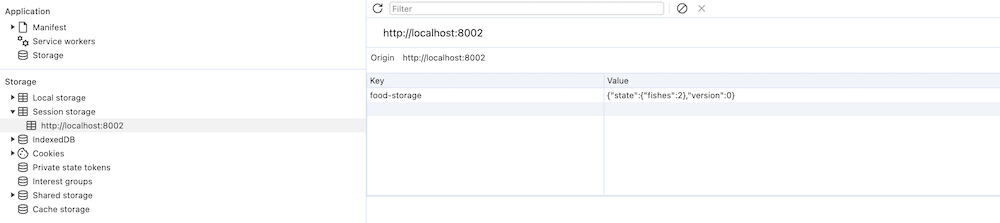
Persist 中间件还有很多配置选项,详情请参考 Persist middleware (opens new window)
# Redux
如果你想要 Redux 风格,可以这样定义 store
// useGrumpyStore.ts
import { create } from 'zustand';
export enum GrumpyType {
Increase = 'Increase',
Decrease = 'Decrease',
}
type Action = {
type: GrumpyType;
by: number;
};
type GrumpyStore = {
grumpiness: number;
dispatch: (args: Action) => void;
};
const reducer = (
state: GrumpyStore,
{ type, by = 1 }: Action,
) => {
switch (type) {
case GrumpyType.Increase:
return { grumpiness: state.grumpiness + by };
case GrumpyType.Decrease:
return { grumpiness: state.grumpiness - by };
}
};
const useGrumpyStore = create<GrumpyStore>()((set) => ({
grumpiness: 0,
dispatch: (args) => set((state) => reducer(state, args)),
}));
export default useGrumpyStore;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
Zustand 提供了 redux 中间件来简化代码
// useGrumpyStore.ts
import { create } from 'zustand';
import { redux } from 'zustand/middleware';
export enum GrumpyType {
Increase = 'Increase',
Decrease = 'Decrease',
}
type Action = {
type: GrumpyType;
by: number;
};
type GrumpyState = {
grumpiness: number;
};
const reducer = (state: GrumpyState, { type, by = 1 }: Action): GrumpyState => {
switch (type) {
case GrumpyType.Increase:
return { grumpiness: state.grumpiness + by };
case GrumpyType.Decrease:
return { grumpiness: state.grumpiness - by };
}
};
const initialState: GrumpyState = {
grumpiness: 0,
};
// 不需要标注 create 函数,也不需要使用 curry 版本
const useGrumpyStore = create(redux(reducer, initialState));
export default useGrumpyStore;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
当使用
redux中间件时不需要标注类型,也不需要使用createcurry 版本,详情请参考 TypeScript Guide (opens new window).
组件使用
const dispath = useGrumpyStore((state) => state.dispatch);
dispath({ type: GrumpyType.Increase, by: 1 }
2
# Redux Devtools
Zustand 提供了 devtools 中间件,通过它可以使用 redux-devtools (opens new window) 工具进行状态监控、调试
import { create } from 'zustand';
import { devtools } from 'zustand/middleware';
type BearStore = {
bears: number;
increase: () => void;
reset: () => void;
};
const useBearStore = create<BearStore>()(
devtools(
(set) => ({
bears: 0,
increase: () =>
set((state) => ({ bears: state.bears + 1 }), false, 'increase'),
reset: () => set({ bears: 0 }, false, 'reset'),
}),
{ name: 'zustand-demo', store: 'BearStore' },
),
);
export default useBearStore;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
有两点需要注意:
需要设置 name 和 store,
name: 'zustand-demo'表示在 devtools 中创建一个名为 "zustand-demo" 的单独实例。store 作为 action 前缀。如果没有使用
redux中间件,action 需要提供 action name,比如上面increase操作的 action name 为 "increase",如果没有提供,默认是 "anonymous"
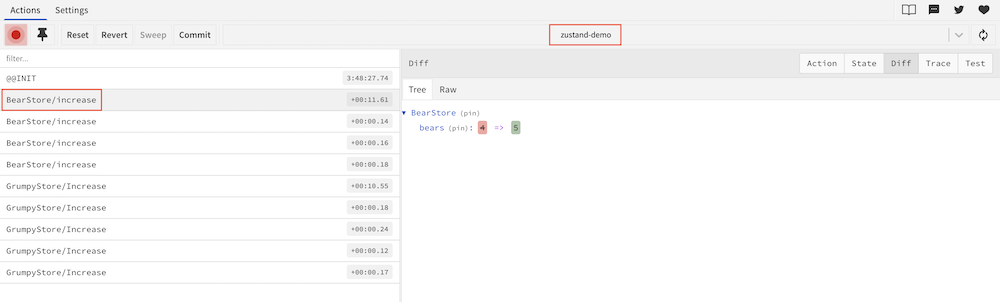
Zustand 推荐把 devtools 中间件放在最后。如果要组合多个中间件可以像下面这样定义一个组合中间件:
import { StateCreator } from 'zustand';
const myMiddlewares = <T>(f: StateCreator<T>) =>
devtools(persist(f, { name: 'bearStore' }), {
name: 'zustand-demo',
store: 'FishStore',
});
type BearStore = {
bears: number;
increase: () => void;
reset: () => void;
};
const useBearStore = create<BearStore>()(
myMiddlewares((set) => ({
bears: 0,
increase: () => set((state) => ({ bears: state.bears + 1 }), false, 'increase'),
reset: () => set({ bears: 0 }, false, 'reset'),
})),
);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# Demo
zustand-demo (opens new window)
# References
Zustand(opens new window)- Zustand Doc (opens new window)
- Zustand vs Others State Libraries (opens new window)
- Auto Generating Selectors (opens new window)
- Slices Pattern (opens new window)
- Persist middleware (opens new window)
- Zustand Third-party Libraries (opens new window)
- Using getter to calculate computed values (opens new window)
Immer(opens new window)- Redux (opens new window)
Redux-devtools(opens new window)- Pinia (opens new window)