# Redux 学习笔记
Redux 是 JavaScript 应用的状态容器,提供可预测的状态管理。一般用于 React 项目中,用于实现全局状态管理。
# Redux Core
首先我们介绍 Redux 的核心概念
# 安装
# NPM
$ npm install redux
# Yarn
$ yarn add redux
2
3
4
5
# 使用 Redux
下面是使用 Redux 的基本流程
// 1. 创建 Reducer
const bankReducer = (state = 0, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'deposit':
return state + action.payload
case 'withdraw':
return state - action.payload
default:
return state
}
}
// 2. 创建 Store
import { createStore } from 'redux'
const store = createStore(bankReducer)
// 3. Dispatch,相当于向 Store 发送一个事件
button.addEventListener('click', () => {
store.dispatch({ type: 'deposit', payload: 10 })
})
// 4. 订阅状态变化
store.subscribe(() => {
// 5. 获取 state,修改元素值
const state = store.getState()
label.innerHTML = state.toString()
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# 数据流
一张图胜过千言万语
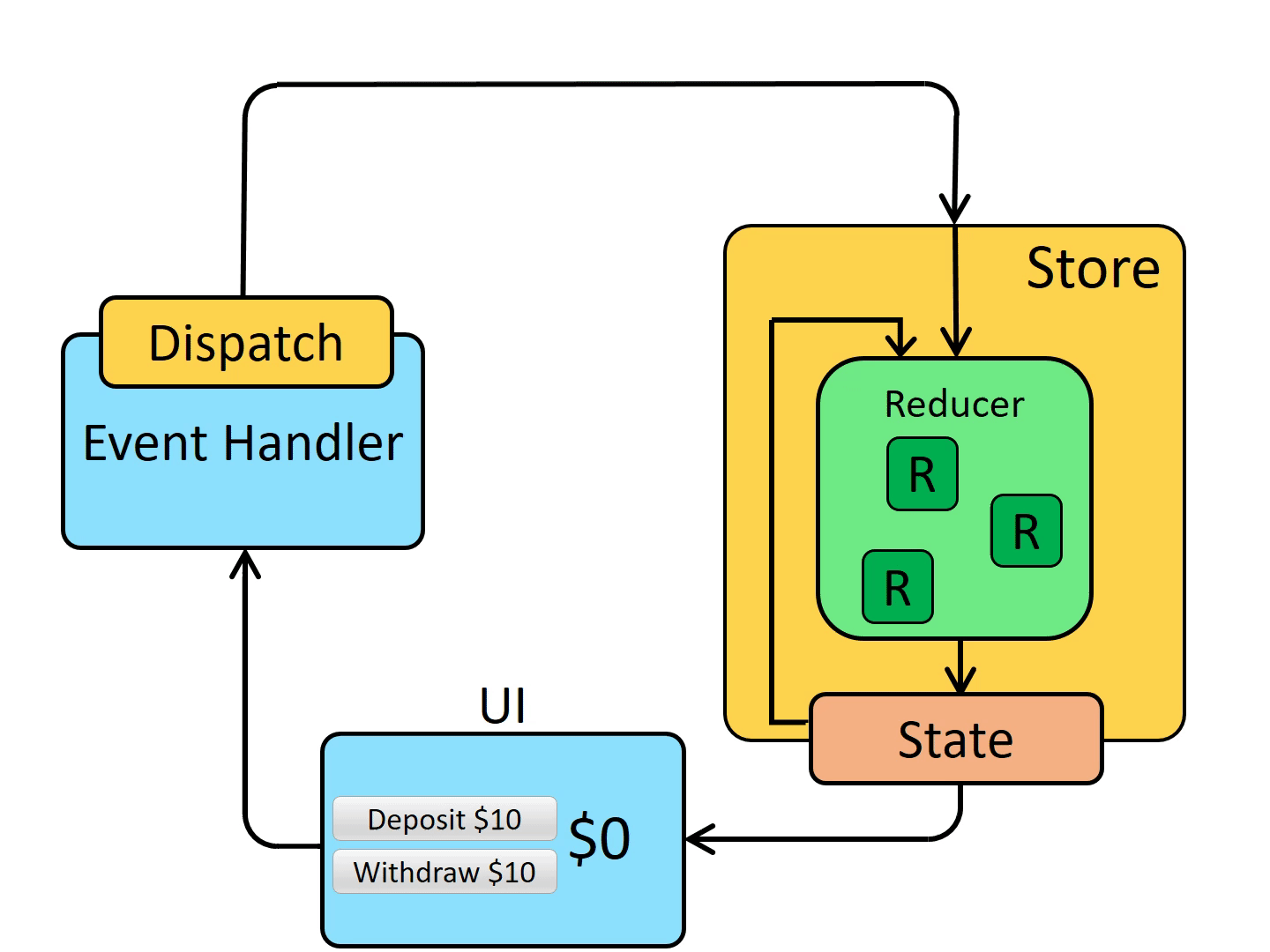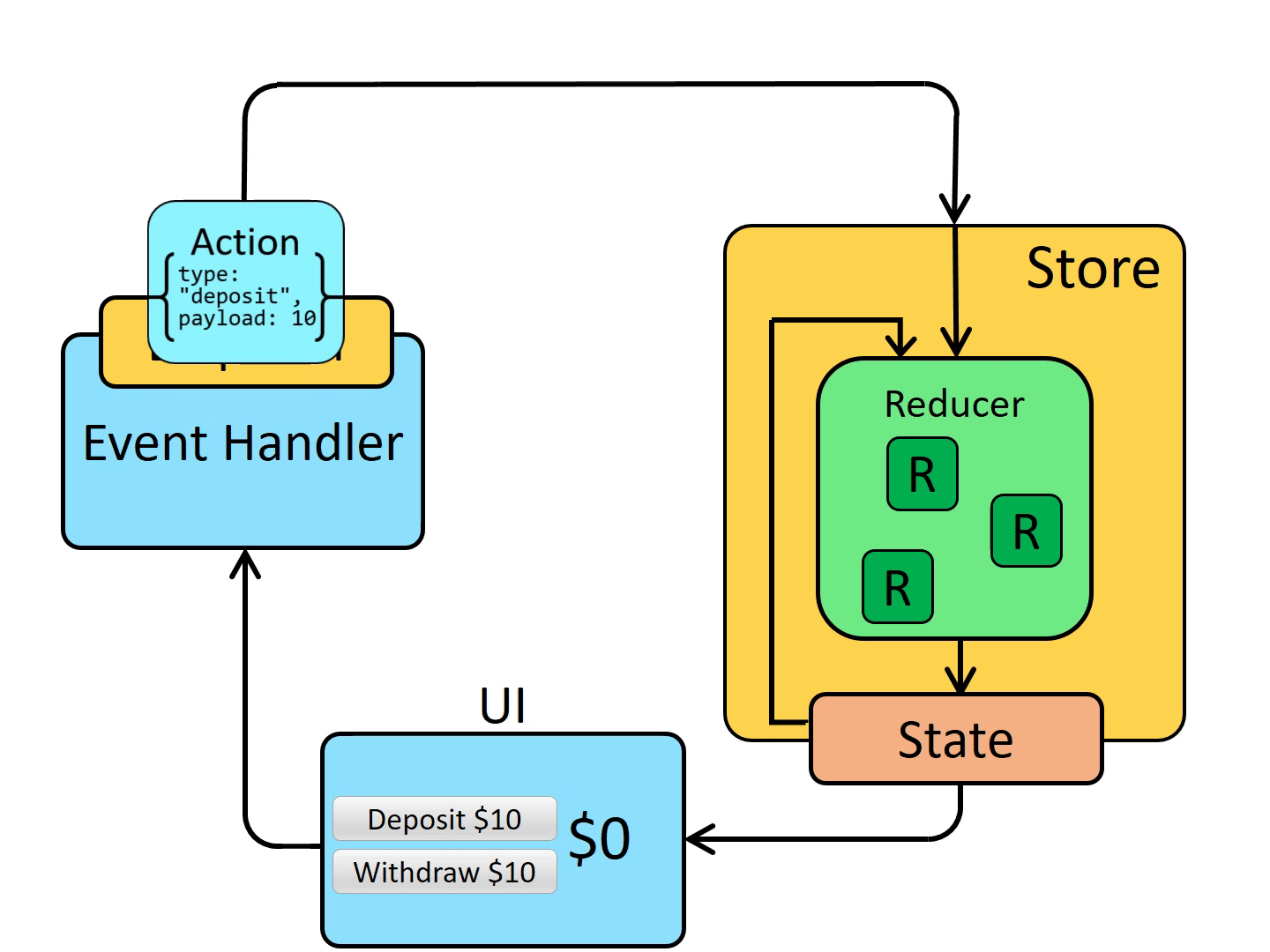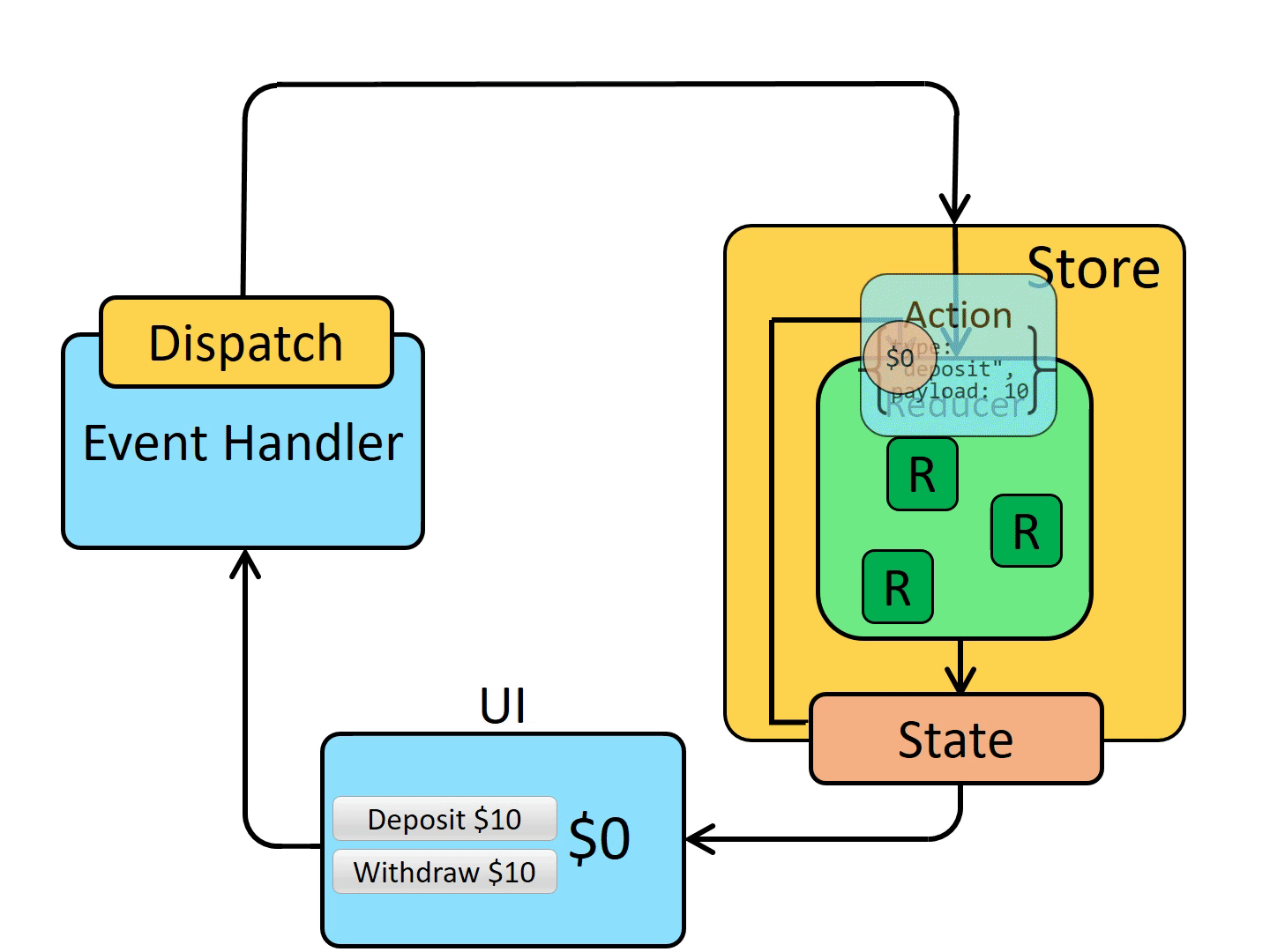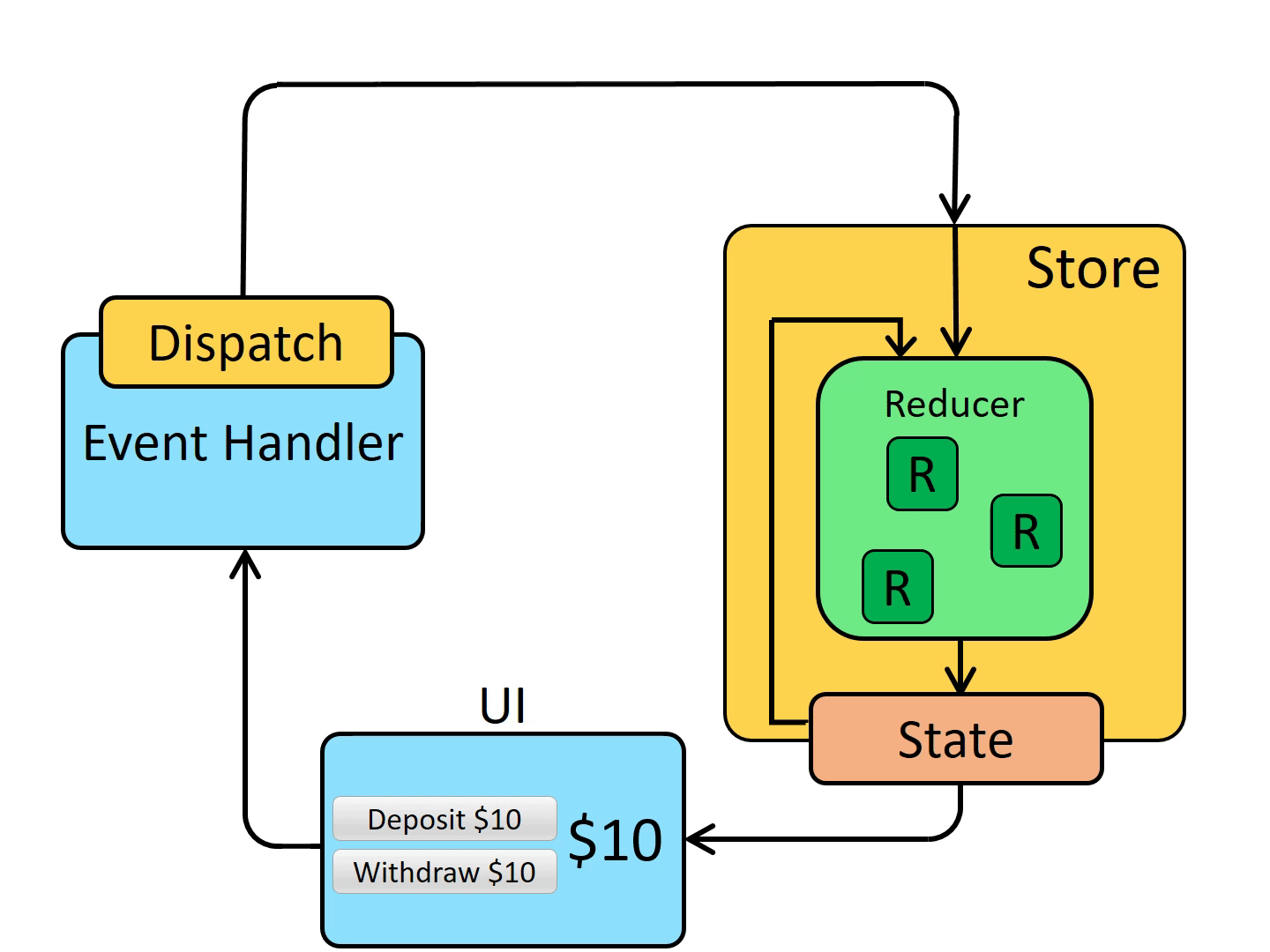
# 核心概念
# Reducer
reducer 是一个函数,接收当前的 state 和一个 action 对象,然后返回新状态。函数签名是:(state, action) => newState。 你可以将 reducer 视为一个事件监听器,它根据接收到的 action 类型处理事件。
const bankReducer = (state = 0, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'deposit':
return state + action.payload
case 'withdraw':
return state - action.payload
default:
return state
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# Action
action 是一个具有 type 字段的普通 JavaScript 对象。你可以将 action 视为描述应用程序中发生了什么的事件。
type 字段是一个字符串,描述事件的类型,action 对象可以有其它字段,包含事件的附加信息,比如 payload。action 对象采用 Flux Standard (opens new window)。
{ type: 'deposit', payload: 10 }
# Store
当前 Redux 应用的状态存在于一个名为 Store 的对象中,通过传入一个 reducer 来创建的 store。
const store = createStore(bankReducer)
Store 对象有三个方法:
# getState
获取当前的 state
store.getState()
# dispatch
更新 state 的唯一方法是调用 dispatch() 并传入一个 action 对象。 store 将执行 reducer 函数并计算出更新后的 state.
store.dispatch({ type: 'deposit', payload: 10 })
dispatch 一个 action 可以形象的理解为 "触发一个事件"。
# subscribe
通过 subscribe 添加一个监听器,当 state 发生变化时,会触发这个监听器。你可以在监听器里调用 getState() 获取当前 state。在 React 项目中可以执行 render 来重绘组件。
store.subscribe(() => {
const state = store.getState()
})
2
3
# Action Creator
action creator 是一个创建并返回一个 action 对象的函数。它的作用是让你不必每次都手动编写 action 对象:
const addTodo = text => {
return {
type: 'todos/todoAdded',
payload: text
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
# Selector
Selector 函数可以从 store 状态树中提取指定的部分。随着应用变得越来越大,会遇到应用程序的不同部分需要读取相同的数据,selector 可以避免重复这样的读取逻辑。
const todoList = state => state.todos
# Combining Reducers
当一个 Redux 项目越来越大时,需要根据 state 树中不同的部分将 reducer 分割成很多个小的 reducer。每个小的 reducer 负责更新 state 树中的一部分内容。然后通过 combineReducers (opens new window) 合并成 root reducer。
作为对比下面是没有使用 combineReducers 的代码
import todosReducer from './features/todos/todosSlice'
import filtersReducer from './features/filters/filtersSlice'
export default function rootReducer(state = {}, action) {
// always return a new object for the root state
return {
// the value of `state.todos` is whatever the todos reducer returns
todos: todosReducer(state.todos, action),
// For both reducers, we only pass in their slice of the state
filters: filtersReducer(state.filters, action)
}
}
const store = createStore(rootReducer)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
使用 combineReducers 大大减少了样板代码
import { combineReducers } from 'redux'
import todosReducer from './features/todos/todosSlice'
import filtersReducer from './features/filters/filtersSlice'
const rootReducer = combineReducers({
todos: todosReducer,
filters: filtersReducer
})
const store = createStore(rootReducer)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# Enhancers
增强器,通过替换 Store 对象的 dispatch、getState 和 subscribe 方法,对 Store 进行一些额外的操作,比如想在每次 dispatch 时,输出 action 日志
增强器的函数签名是:
(createStore) => (rootReducer, preloadedState, enhancers) => new Store
const logOnDispatch = (createStore) => (rootReducer, preloadedState, enhancers) => {
const store = createStore(rootReducer, preloadedState, enhancers)
function newDispatch(action) {
const result = store.dispatch(action)
console.log(action)
return result
}
return { ...store, dispatch: newDispatch }
}
// 然后在创建 Store 时,将 enhancer 传入第三个参数上
const store = createStore(rootReducer, undefined, logOnDispatch)
// 如果没有初始值 `preloadedState`,可以将 enhancer 传入第二个参数上
const store = createStore(rootReducer, logOnDispatch)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
或者每次获取 state 时,添加额外的属性 meaningOfLife
const includeMeaningOfLife = (createStore) => (rootReducer, preloadedState, enhancers) => {
const store = createStore(rootReducer, preloadedState, enhancers)
function newGetState() {
return {
...store.getState(),
meaningOfLife: 42,
}
}
return { ...store, getState: newGetState }
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# compose
如果同时添加多个 enhancer 怎么办呢?Redux 提供了 compose (opens new window) 方法
import { compose } from 'redux'
const composedEnhancer = compose(logOnDispatch, includeMeaningOfLife)
const store = createStore(rootReducer, undefined, composedEnhancer)
2
3
4
# Middleware
中间件在 dispatch action 和 action 到达 reducer 之间提供了一个第三方扩展。我们可以使用 Redux middleware 进行日志记录、崩溃报告、异步 API 请求、路由等。和 reducer 不一样,middleware 可以有 side effects (opens new window)。
Middleware 的函数签名:(storeAPI) => (next) => (action) => {}
const exampleMiddleware = storeAPI => next => action => {
// pass the action onwards with next(action),
// or restart the pipeline with storeAPI.dispatch(action)
return next(action)
}
2
3
4
5
middleware 解析:
storeAPI: 一个包含 Storedispatch和getState方法的对象,即 { dispatch, getState },非 Store 对象next:下一个 middleware 或者是初始的store.dispath方法- 调用
next(action)将 action 传给下一个 middleware 或者初始的store.dispath方法 - 调用
storeAPI.dispatch重启 pipeline - 应用 middleware 之后,
store.dispath返回的是第一个middleware 返回的值,初始的store.dispath方法返回 action 对象
# 定义 middleware
export const print1 = (storeAPI) => (next) => (action) => {
console.log('1')
return next(action)
}
export const print2 = (storeAPI) => (next) => (action) => {
console.log('2')
return next(action)
}
export const print3 = (storeAPI) => (next) => (action) => {
console.log('3')
return next(action)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# 使用 middleware
Redux 通过 applyMiddleware (opens new window) 将多个 middleware 合成一个 enhancer
import { applyMiddleware } from 'redux'
import { print1, print2, print3 } from './middleware'
const middlewareEnhancer = applyMiddleware(print1, print2, print3)
const store = createStore(rootReducer, middlewareEnhancer)
store.dispatch({ type: 'todos/todoAdded', payload: 'Learn about actions' })
// log: '1'
// log: '2'
// log: '3'
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# Pipeline
Redux middleware 围绕 store.dispath 方法形成一个 pipeline.
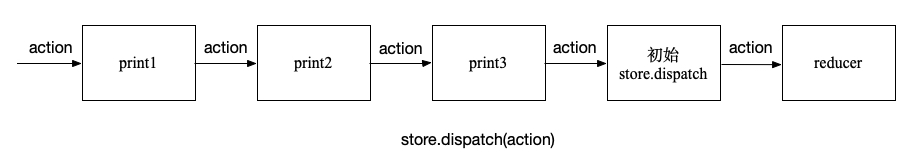
# React Devtools
为了让 Redux DevTools (opens new window) 能调试我们的 Store,我们需要添加 redux-devtools-extension
# 安装
npm install --save @redux-devtools/extension
# 配置
使用 composeWithDevTools 代替之前的 Redux 的 compose 方法
import { composeWithDevTools } from 'redux-devtools-extension'
const composedEnhancer = composeWithDevTools(
// 这里可以添加任意 middleware
applyMiddleware(print1, print2, print3)
// 这里可以添加任意 enhancer
// ...
)
const store = createStore(rootReducer, composedEnhancer)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# Thunk
Redux 使用 middleware 来处理异步逻辑,比如网络请求
我们首先写一个异步函数 middleware
const asyncFunctionMiddleware = storeAPI => next => action => {
if (typeof action === 'function') {
// 如果 action 是函数,则直接调用 action 函数,参数是 dispatch 和 getState 方法
return action(storeAPI.dispatch, storeAPI.getState)
}
// 否则传给下一个 middleware
return next(action)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
然后我们可以这样使用这个 middleware
const middlewareEnhancer = applyMiddleware(asyncFunctionMiddleware)
const store = createStore(rootReducer, middlewareEnhancer)
// Write a function that has `dispatch` and `getState` as arguments
const fetchSomeData = (dispatch, getState) => {
// Make an async HTTP request
client.get('todos').then(todos => {
// Dispatch an action with the todos we received
dispatch({ type: 'todos/todosLoaded', payload: todos })
// Check the updated store state after dispatching
const allTodos = getState().todos
console.log('Number of todos after loading: ', allTodos.length)
})
}
// 这里的 action 是函数,即 thunk
store.dispatch(fetchSomeData)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
加入异步逻辑之后,Redux 的数据流是这样的
# Redux Thunk
为了简化异步函数 middleware 的创建,Redux 提供了官方的 thunk 库 - Redux Thunk (opens new window)
# 安装
$ npm install redux-thunk
# 配置
import thunkMiddleware from 'redux-thunk'
const composedEnhancer = composeWithDevTools(applyMiddleware(thunkMiddleware))
const store = createStore(rootReducer, composedEnhancer)
2
3
4
有了 redux-thunk,我们就可以写 Thunk 函数了。Thunk 函数可以包含任何我们想要的异步逻辑
function thunkFunction = (dispatch, getState) => {
// 可以 dispatch action
// 还可以 get state
}
2
3
4
上面的 fetchSomeData就是一个典型的 Thunk 函数
The word "thunk" is a programming term that means "a piece of code that does some delayed work" (opens new window). For more details on how to use thunks, see the thunk usage guide page:
as well as these posts:
# Memoized Selectors
如果使用下面的 selector 从 state 挑选需要的数据,因为 array.map() 总是返回一个新的数组,在每次 dispatch 后都会运行 React-Redux useSelector hook,返回的新数组将导致组件重新渲染(即使数组的值没有变化),影响性能
const selectTodoIds = state => state.todos.map(todo => todo.id)
为了解决这个问题,可以使用 Reselect (opens new window) 库提供的 createSelector 方法
# 安装
$ npm install reselect
# 使用
import { createSelector } from 'reselect'
import { useSelector } from 'react-redux'
export const selectTodoIds = createSelector(
state => state.todos,
todos => todos.map(todo => todo.id)
)
const todoIds = useSelector(selectTodoIds)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
createSelector 接收多个 input 函数和一个 output 函数,input 函数的返回值作为 output 函数的参数,当 input 函数的返回值没有变化时,output 函数不会运行,重用上一次 output 函数的返回值。
# Normalized State
出于 性能考虑 (opens new window), Redux 项目一般采用 normalized state (opens new window) 存储数据,什么是 normalized state?
- 我们 state 中的每个特定数据只有一个副本,不存在重复。
- 数据保存在查找表中,其中项目 ID 是键,项本身是值。
- 也可能有一个特定项用于保存所有 ID 的数组。
下面这个就是 normalized state
{
users: {
ids: ["user1", "user2", "user3"],
entities: {
"user1": {id: "user1", firstName, lastName},
"user2": {id: "user2", firstName, lastName},
"user3": {id: "user3", firstName, lastName},
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# Redux Toolkit
Redux 推荐使用 Redux Toolkit 来简化 Redux 操作,减少样板代码。
- 集成了 Redux Thunk (opens new window)、Reselect (opens new window) 和 Redux Devtools Extension (opens new window),简化了对 Store 的配置
- 使用 Immer (opens new window),简化了 reducer 更新 state 的操作
createAsyncThunk(),简化异步请求createEntityAdapter()实现 Normalized State
# 安装
npm install @reduxjs/toolkit
# configureStore()
使用 configureStore() 简化 store 的配置流程
import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
import todosReducer from './features/todos/todosSlice'
import filtersReducer from './features/filters/filtersSlice'
const store = configureStore({
reducer: {
// Define a top-level state field named `todos`, handled by `todosReducer`
todos: todosReducer,
filters: filtersReducer
}
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
对比 Redux 的 createStore(), configureStore() 做了下面这些事情
- 将多个小的 reducers 组合成一个 roote reducer,而
createStore()需要使用combineReducers()来组合 reducers - 自动添加了 Thunk middleware
- 自动建立了 Redux DevTools Extension 连接
- 自动添加了更多的 middleware 来检查常见错误,比如意外改变 state
# createSlice()
使用 createSlice() 简化 reducer。
- 使用函数替换
switch/case语句 - 内部使用了 Immer (opens new window),可以直接修改 state
- 自动生成 action creators
import { createSlice } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
const initialState = []
const todosSlice = createSlice({
name: 'todos', // action type 的前缀
initialState, // 初始值
reducers: {
todoAdded(state, action) {
// 可以直接修改 state
state.push(action.payload)
},
todoToggled(state, action) {
const todo = state.find(todo => todo.id === action.payload)
todo.completed = !todo.completed
},
}
})
// 自动生成 action creators
export const { todoAdded, todoToggled } = todosSlice.actions
// 导出 reducer
export default todosSlice.reducer
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
自动生成的 action creators 是什么样的呢?
console.log(todoToggled(42))
// {type: 'todos/todoToggled', payload: 42}
2
action.type 是 slice 的 name + 方法名,而 action.payload 是函数参数
# createAsyncThunk()
Redux Toolkit 集成了 Redux Thunk (opens new window),我们可以直接通过 Thunk 函数书写异步逻辑。
同时 Redux Toolkit 提供了 createAsyncThunk() 方法简化了异步请求。
因为一般的异步请求可以概括为三个状态
- 请求中:pending
- 请求成功:fulfilled
- 请求失败:rejected
import { createAsyncThunk } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
export const fetchTodos = createAsyncThunk('todos/fetchTodos', async () => {
const response = await client.get('/fakeApi/todos')
return response.todos
})
2
3
4
5
6
createAsyncThunk() 方法接收两个参数
- 生成的 action type 的前缀(
todos/fetchTodos) - 一个回调函数执行网络请求,要求返回一个 Promise,一般我们使用 async function。这个函数有两个参数
- 第一个是
createAsyncThunk()返回的函数传入的参数。 - 第二个是
{getState, dispatch}
- 第一个是
createAsyncThunk() 返回一个 thunk 函数.
store.dispatch(fetchTodos())
createAsyncThunk() 自动生成三个 action creator.
fetchTodos.pending:todos/fetchTodos/pending`fetchTodos.fulfilled:todos/fetchTodos/fulfilledfetchTodos.rejected:todos/fetchTodos/rejected
因为生成的 ation creators 不在 createSlice 里,因此需要通过在 extraReducers option 使用 builder.addCase(actionCreator, caseReducer),监听这些 action types。
const todosSlice = createSlice({
name: 'todos',
initialState,
reducers: {
// omit reducer cases
},
extraReducers: builder => {
builder
.addCase(fetchTodos.pending, (state, action) => {
state.status = 'loading'
})
.addCase(fetchTodos.fulfilled, (state, action) => {
state.entities = action.payload
state.status = 'succeeded'
})
.addCase(fetchTodos.rejected, (state, action) => {
state.status = 'failed'
state.error = action.error.message
})
}
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
builder 对象提供了一些方法,让我们可以定义额外的 case reducer,这些 reducer 将响应在 slice 之外定义的 action:
builder.addCase(actionCreator, reducer):定义一个 case reducer,它响应 RTK action creator 生成或者普通字符串定义的 action。builder.addMatcher(matcher, reducer):定义一个 case reducer,它可以响应任何matcher函数返回true的 action.builder.addDefaultCase(reducer):定义一个 case reducer,如果没有其他 case reducer 被执行,这个 action 就会运行。
您可以将这些链接在一起,例如builder.addCase().addCase().addMatcher().addDefaultCase()。 如果多个匹配器匹配操作,它们将按照定义的顺序运行。
# createEntityAdapter()
Redux Toolkit 提供 createEntityAdapter() 方法实现 Normalized State,它获取集合并将它们放入 { ids: [], entities: {} } 的结构中。
createEntityAdapter() 返回一个 adapter 对象,这个对象包含多个预置函数,用来处理一些常见的情况,这些函数可以用于 reducer 函数中。
addOne/addMany: 添加一个或多个 itemsupdateOne/updateMany: 更新一个或多个 itemsupsertOne/upsertMany: 添加或更新一个或多个 itemsremoveOne/removeMany: 根据 ids 删除一个或多个 itemssetAll: 替换所有的数据
此外 adapter 对象还有两个函数
getInitialState: 返回对象{ ids: [], entities: {} },可以传入参数,将参数组合到这个对象里getSelectors: 生成标准的 selector 函数- selectAll:返回所有的 items
- selectById:返回 id 对应的 item
- selectIds:返回所有的 ids
# Demo
import { createEntityAdapter } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
// `createEntityAdapter` 接收一个比较函数,用于数组排序
const postsAdapter = createEntityAdapter({
sortComparer: (a, b) => b.date.localeCompare(a.date)
})
// 返回 { ids: [], entities: {}, status: 'idle', error: null }
const initialState = postsAdapter.getInitialState({
status: 'idle',
error: null
})
const postsSlice = createSlice({
name: 'posts',
initialState,
reducers: {
// omit reducer cases
},
extraReducers(builder) {
// omit other reducers
builder
.addCase(fetchPosts.fulfilled, (state, action) => {
state.status = 'succeeded'
// 使用 postsAdapter.upsertMany 添加或更新多个 items
postsAdapter.upsertMany(state, action.payload)
})
// 使用 postsAdapter.addOne 添加一个 item
.addCase(addNewPost.fulfilled, postsAdapter.addOne)
}
})
export const {
selectAll: selectAllPosts,
selectById: selectPostById,
selectIds: selectPostIds
} = postsAdapter.getSelectors(state => state.posts)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
# React Redux
React Redux (opens new window) 是官方的 React UI 绑定层。它允许 React 组件从 Redux store 读取数据、dispatch action 去更新 state。
# 安装
$ npm install react-redux
# 注入 Store
React Redux 要求组件不能引入 store 对象,而是通过 Provider 组件注入到整个应用中,这样在组件里就可以使用 React Redux 提供的 hooks 访问 store 了。
// in src/index.js
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
import { Provider } from 'react-redux'
import App from './App'
import store from './store'
ReactDOM.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>
</React.StrictMode>,
document.getElementById('root')
)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# useStore()
React Redux 使用 useStore() 获取所需注入的 store
import { useStore } from 'react-redux'
const store = useStore()
2
# useSelector()
React Redux 使用 useSelector() 获取所需的 state 数据,useSelector() 接收 selector,返回 state 数据。
import React from 'react'
import { useSelector } from 'react-redux'
import TodoListItem from './TodoListItem'
const selectTodos = state => state.todos
const TodoList = () => {
const todos = useSelector(selectTodos)
const renderedListItems = todos.map(todo => {
return <TodoListItem key={todo.id} todo={todo} />
})
return <ul className="todo-list">{renderedListItems}</ul>
}
export default TodoList
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
每次 dispatch action 时,useSelector() 将重新执行,如果返回的值发生变化,则强制 React 组件重新绘制。useSelector() 使用 === 进行 reference 标记,如果 useSelector() 返回不同的 reference,将影响性能,例如
const todoIds = useSelector(state => state.todos.map(todo => todo.id))
一个解决办法是使用 Redux 提供的 shallowEqual() 方法,比较数组内容是否发送变化。
import React from 'react'
import { useSelector, shallowEqual } from 'react-redux'
import TodoListItem from './TodoListItem'
const selectTodoIds = state => state.todos.map(todo => todo.id)
const TodoList = () => {
const todoIds = useSelector(selectTodoIds, shallowEqual)
const renderedListItems = todoIds.map(todoId => {
return <TodoListItem key={todoId} id={todoId} />
})
return <ul className="todo-list">{renderedListItems}</ul>
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
另一个解决办法是使用 Memoized Selectors
# useDispatch()
React Redux 使用 useDispatch() dispatch action
import React from 'react'
import { useDispatch } from 'react-redux'
const Header = () => {
const dispatch = useDispatch()
const onClick = () => {
dispatch({ type: 'todos/add', payload: 10 })
}
return (
<button onClick={onClick}>Dispath</button>
)
}
export default Header
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15